COMPUTER HISTORICAL BACK GROUND
To most people, computers are just electronic devices that offer a means of accessing Internet. Most of us do not know that computers were designed as large calculating machines. Before World War II, the term computer was applied as a job title to the human clerks (performed routine computations for business,governments and research purposes).
The earliest data processing equipment were all manual-mechanical devices due to the absence of electricity and adequate industrial technology. A manual – mechanical device is powered by hand and it requires physical effort. An electro-mechanical device is powered by electric motor and uses switches and relays. An electronic device has principal component circuit boards, transistors or silicon chips.
Mechanical Age
During this age, calculations were first
performed using Punched Cards. Then Abacus came into existence, which consisting
of strings of beads to perform calculations. Later, Mechanical Calculator was
invented by Blaire Pascal in1642. This calculator was constructed with gears
and wheels. Then, a Mechanical Computer was brought by Charles Babbage in 1837.
Electrical Age
With the invention of an Electrical Motor in the
19th Century, the electrically driven mechanical calculators were developed. These
calculators were better than
mechanical calculators but still disadvantageous in terms of speed and reliability
Electronic Age
In the year 1946, Vacuum tubes were invented. In
the same year, electronic computer using vacuum tubes named ENIAC was invented.
ENIAC (Electronic Numeric Integrator And Calculator).
o This can perform
100,000 operations per second.
o For changing the program, it requires rewiring the circuitry.
o It is faster than electrically driven mechanical calculator and highly reliable
Generations of Computers
‘Generation’ in computer terminology is a ‘step’ ahead in technology. As you go through the history of evolution of computers, you will find that the earliest computers were big in size, consumed a lot of power and heated up quickly, due to which it had to be shut down, frequently to be cooled.They were very expensive in terms of development and maintenance.
First Generation Computers (1940 to 1956)
The first generation of computers was characterized by vacuum tubes in the circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. These computers were enormous in size, used great deal of electricity and were expensive to operate. They also had limited storage capacity. Early computers like ENIAC, EDVAC and UNIVAC can all be classified as first generation computers.
 |
| First Generation Computers |
Second Generation Computers (1956 to
1963)
In the early 1950s, the discoveries of Transistor and Magnetic core memory changed the image of computers – from unreliable to highly reliable machines with increased capability, and higher storage capacity. These machines were expensive to purchase and operate and were, therefore, mostly found in large computer centres or government/private laboratories with many programmers and support professionals.
Third Generation Computers (1964 to 1971)
Was largely characterized by the development of integrated circuits Computer manufacturers could provide a range of accessories like the cathode ray tube display devices, page printers, consoles etc. Existence of an operating system allowed the device to run various applications at one time with the central program monitoring the memory. For the first time, computers were being widely used in business for areas like :
- Accounting
- Payroll
- Billing
- Tracking Inventory, etc
Fourth Generation Computers (1971 to present)
The trend in 1970s was to move from single-purpose but powerful computers towards cheaper computer systems that could support a large range of applications. A new revolution in computer hardware came about which could shrink the computer logic circuitry and its components using the Large Scale Integration (LSI) technology. Hundreds of components could now fit onto a single chip!
In the 1980s, Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) squeezed
hundreds of
thousands of components onto a single chip
Fifth Generation Computers (the Road Ahead)
The fifth generation of computers
characterized by artificial intelligence is in the process of development. The
goal here is to develop devices that are capable of learning and responding to
natural language input. This generation of computers is using new technologies
in very large scale integration, along with new programming languages and will
be capable of amazing feats, in the area of artificial intelligence, such as
voice recognition.
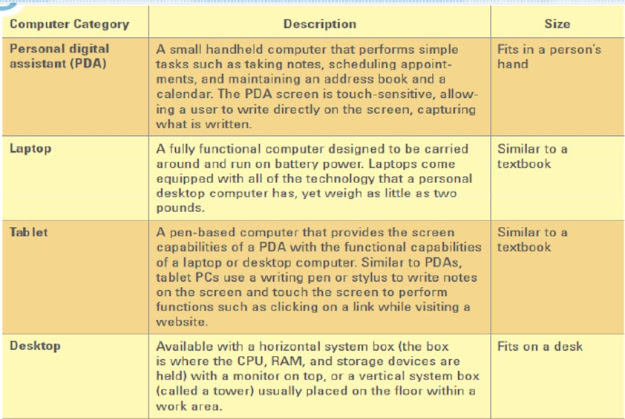
Computer Categories
Definition of a computer
Concise Oxford English Dictionary
(2004) defines computer as an electronic device which
is capable of receiving
information (data) and performing a sequence
of logical operations
in accordance with a predetermined but variable set of
procedural instructions
(program) to produce a
result in the form
of information or signals.In other words, it is a machine that stores programs and information in electronic form and can be used for a variety of processes, for example writing, calculating, and communicating on the Internet
The computer system consists of three units:
1. Input device Units
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
3. Output device Units
Major Functions of a computer
1) It accepts data or instruction by way of input,
2) It stores data,
3) It can process data as required by the user
4) It gives results in the form of output, and
5) It controls all operations inside a computer.
Computer components
 |
|
1. Scanner |
9. Speakers |
|
2. CPU (Microprocessor) |
10. Monitor |
|
3. Primary storage (RAM) |
11. System software |
|
4. Expansion cards (graphics, etc.) |
12. Application software |
|
5. Power supply |
13. Keyboard |
|
6. Optical disc drive |
14. Mouse |
|
7. Secondary storage (Hard disk) |
15. External hard disk |
|
8. Motherboard |
16. Printer |
Input Devices
Input devices are used to accept data and instructions from the user.
Examples of various input devices, which are connected to the computer.
1.
Keyboard 2. Mouse 3. Light Pen
4.
Optical/magnetic Scanner 5. Touch Screen
6.
Microphone 7. Track Ball
1. Keyboard
A keyboard is
the most common input device. The keyboard in most common use is the QWERTY
board. Generally standard keyboard has 104 keys.
2. Mouse
A mouse is an
electro-mechanical, hand-held device. It is used as a pointer. It can perform functions
like selecting menu commands, moving icons, resizing windows, starting
programs, and choosing options
3. Light pen
An input
device that utilizes a light-sensitive detector to select objects on a display
screen. A light pen is similar to a mouse, except that with a light pen you can
move the pointer and select objects on the display screen by directly pointing to
the objects with the pen.
4. Optical Scanner
These devices
are used for automatic data collection. The devices of this category completely
eliminate manual input of data. For example, the bar-code reader is actually
just a special type of image scanner.
5. Touch Screen
Touch panel displays and pads are now being offered as alternatives to keyboard. Here the input can be given through the computer screen, that accepts the input through monitor; users touch electronic buttons displayed on the screen or they may use light pen.
6. Microphone
Microphone is
an input device, which takes voice as input. The voice communication is more
error-prone than information through keyboard
7 Track Ball
Trackball, a pointing device, is a mouse lying on its back. To move the pointer, you rotate the ball with your thumb, your fingers, or the palm of your hand.
Output Devices
Output
devices return processed data that is information, back to the user. Some of
the commonly used output devices are:
1.
Monitor (Display Screen)
2.
Printers
3.
Plotter
4.
Speakers
5. Projectors
1. Monitor (Display Screen)
It is used to
display visually information processed within the CPU. Most monitors have a
resolution of at least 800 x 600 pixels. High-end monitors can have resolutions
of 1024 x 768 pixels or even 1280 x 1024 pixels. Thus monitors are available
either in low resolution or in high resolution
2. Printer
A printer
is used to transfer data from a computer onto paper. The paper copy
obtained from a printer is often referred as printout.
3 Plotter
A plotter is a
special kind of output device that, like a printer, produces images on paper,
but does so in a different way. Plotters are designed to produce large drawings
or images, such as construction plans for buildings or blueprints for mechanical
objects. A plotter can be connected to the port normally used by a printer.
4. Speakers
Speakers are another type of output device, which allow you to listen
to voice like music, and conversation with people.
6. Projector
An output device that can take the display of
a computer screen and project a large version of it onto a flat surface. Projectors are often used in meetings and presentations
to help make sure everyone in the room can view the presentation


















No comments:
Post a Comment